Primary Parting Plane Runners
In many cases, the mold design dictates the gating position, although ideally, the optimum gate position should be determined based on part requirements and afterwards the mold design should be selected to provide for the gate desired position.
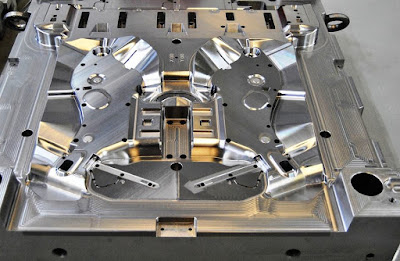
Available gating positions, and gate designs, are significantly influenced by whether the runner travels along the primary parting plane of the mold (the parting plane where the part forming cavity is defined) or whether it does not travel along this plane.
In the dominant runner type used in the industry the runner and part forming cavities are located along the same primary parting plane.
Primary parting planes, often referred to as the parting lines, are where the mold opens and closes to allow ejection of the molded part and/or of the runner. The primary parting plane is the one where the molded part is formed and ejected. The primary parting plane runner is used in two plate cold runner molds.
A cold runner mold is defined as a mold in which the plastic. material in the runner is cooled and ejected from the mold during each mold cycle.
Molten plastic material is injected through the runner, the gate, and then into the part-forming cavity. This molten plastic is then cooled by the mold, and when sufficiently solidified, the mold opens and the runner, gate, and part are ejected along the same primary parting plane.
Notice that the part and runner are formed and ejected along the same parting plane.
After the molded part and runner are ejected, the mold again closes, creating a flow channel (runner path) between the injection molding machine nozzle to the part forming cavity.
As the primary parting plane runner is located along the same parting plane as the part forming cavity, gating into the part is limited to its perimeter, or very near its perimeter. Sub gates, such as the tunnel, cashew and jump gates, allow gating to be positioned within a short distance from the actual perimeter of the part
Available gating positions, and gate designs, are significantly influenced by whether the runner travels along the primary parting plane of the mold (the parting plane where the part forming cavity is defined) or whether it does not travel along this plane.
In the dominant runner type used in the industry the runner and part forming cavities are located along the same primary parting plane.
Primary parting planes, often referred to as the parting lines, are where the mold opens and closes to allow ejection of the molded part and/or of the runner. The primary parting plane is the one where the molded part is formed and ejected. The primary parting plane runner is used in two plate cold runner molds.
A cold runner mold is defined as a mold in which the plastic. material in the runner is cooled and ejected from the mold during each mold cycle.
Molten plastic material is injected through the runner, the gate, and then into the part-forming cavity. This molten plastic is then cooled by the mold, and when sufficiently solidified, the mold opens and the runner, gate, and part are ejected along the same primary parting plane.
Notice that the part and runner are formed and ejected along the same parting plane.
After the molded part and runner are ejected, the mold again closes, creating a flow channel (runner path) between the injection molding machine nozzle to the part forming cavity.
As the primary parting plane runner is located along the same parting plane as the part forming cavity, gating into the part is limited to its perimeter, or very near its perimeter. Sub gates, such as the tunnel, cashew and jump gates, allow gating to be positioned within a short distance from the actual perimeter of the part
评论